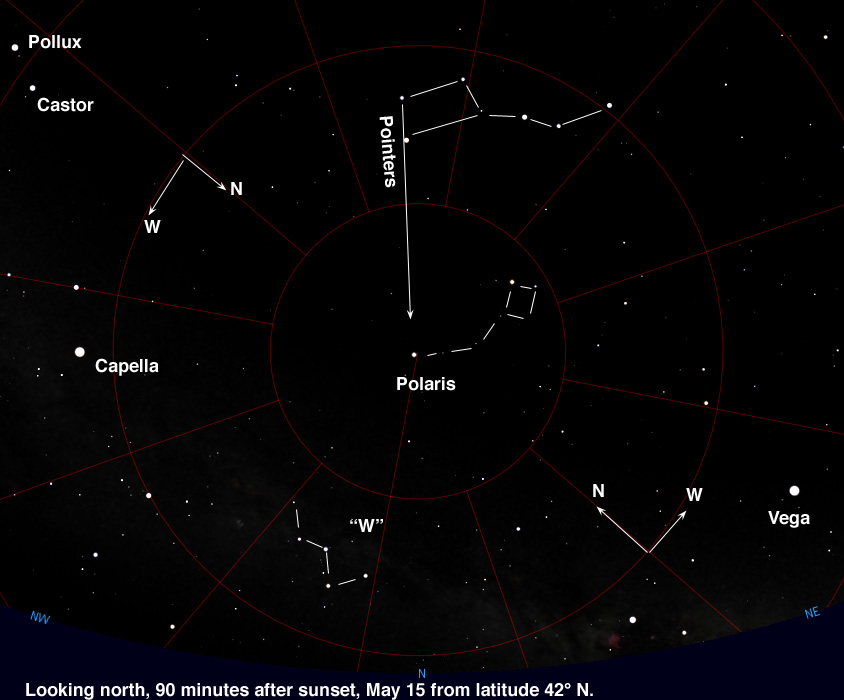
Star: Polaris
Constellation: Little Bear and Little Dipper
Location:
Right Ascension: 2h31m48.704s
Declination: +89°15'50.72"
Stellar Classification: F(F7) yellow supergiant
Chemical Makeup: metals including magnesium, calcium, titanium, iron, strontium
Spectrum analysis: magnesium
http://www.solarsystemquick.com/universe/find_polaris.jpg
https://astrojourney.files.wordpress.com/2010/04/north_may_2010.jpg
Sources:
List of brightest stars. (2013). Retrieved September 28, 2015, from http://www.astronoo.com/en/brightest-stars.html
Stars. (2013). Retrieved September 28, 2015, from http://www.astronoo.com/en/stars.html
Kaler, J. (n.d.). Polaris. Retrieved September 30, 2015, from http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/polaris.html
Howell, E. (2015, February 11). What Are The Most Famous Stars? Retrieved September 30, 2015, from http://www.universetoday.com/45775/famous-stars/


No comments:
Post a Comment